By the end of this report, understand the opportunity in AI Browsers and present progress by looking at the launched AI browsers and gaps in the AI browser market.
Note: This is out first AI trend analysis report – please suggest improvements in comments.
Key takeaways about the AI Browser opportunity:
- A fundamental shift in web browsing behavior – Users are moving from passive content consumption. They now expect active, intelligent assistance with AI-synthesized answers and personalized experiences.
- Intense market competition – Both tech giants and startups are competing to integrate core AI capabilities directly into browsers. Venture funding is shifting toward deep technology infrastructure rather than surface-level AI applications.
- Privacy and ethics as competitive differentiators – Successfully navigating privacy concerns is now essential for market success. Ethical considerations are also crucial. Meeting regulatory compliance has become a key way companies distinguish themselves.
Problem statement: Why current browsing experience fail?
Legacy browser design was optimized for static page consumption. It can’t efficiently handle today’s information-overloaded environment. It also struggles with repetitive tasks, personalization needs, and privacy expectations.
Solution statement: What are AI browsers?
AI browsers are intelligent web platforms that integrate artificial intelligence into the browsing experience. The AI helps personalize, automate, and simplify content consumption as you navigate the internet. Using intelligent algorithms, AI browsers continuously learn from user interactions to deliver personalized and real-time assistance. This transforms passive browsing into a proactive and efficient interaction.
How do AI browsers work?
The solutions provided by AI browsers represent a fundamental shift in the interaction model. They transition from a “pull” paradigm—where users actively search and navigate—to a “push” or “predictive” model.
In this new model, AI anticipates user needs and proactively delivers synthesized information or automates actions. This is clear in features like Dia’s ability to remember earlier interactions and adapt its responses. Or the predictive assistance offered by AI browser tools that continuously learn from interactions.
This evolution means AI browsers are not merely enhanced search tools. They are becoming proactive digital assistants. These assistants are designed to reduce user effort and cognitive load. AI browsers will fundamentally redefine the online experience.
10 key features of AI browsers to look for:
- Intelligent learning: AI browsers continuously learn from user interactions to give personalized, real-time assistance tailored to individual preferences and behaviors.
- Smart search and summarization: Advanced algorithms deliver more relevant search results. They also allow one-click content summarization to cut through information overload.
- Automated web tasks: AI browsers can automatically execute repetitive tasks. These include form filling, data extraction, and multi-step workflows. They can also bypass anti-bot defenses.
- Enhanced privacy protection: On-device AI processing minimizes the need to send sensitive data to external servers. This significantly improves user privacy and security.
- Integrated AI assistance: Native AI assistants are built directly into the browser interface. They allow users to chat with tabs, compare content, and draft text. All this can be done without leaving their current page.
- Predictive user support: AI browsers expect user needs. They proactively deliver synthesized information. They also automate actions before users explicitly ask for them.
- Dynamic content adaptation: Content and interfaces adapt in real-time to user preferences, creating a more responsive and personalized browsing experience.
- Contextual Writing Assistance: Sophisticated writing tools help users draft content in specific tones and styles directly within the browser environment.
- Intelligent Tab Management: AI-powered features like smart tab grouping and contextual organization help users manage complex browsing sessions more efficiently.
- Seamless Multi-Step Automation: Advanced AI agents can execute complex web tasks. They manage multi-step processes at scale while navigating sophisticated website defenses. They also overcome security measures.
Macro trends driving AI browser need and adoption

The Shift from Automation to Adaptation and Agentic Workflows
AI has evolved from simple task automation to sophisticated adaptation that aligns with human workflows. Users become “orchestrators” rather than “doers,” with AI agents capable of reasoning, delegating, and routing across tools. For example, AI Coding Tools like Claude Code or Lovable exemplify this shift by completing complex coding tasks with minimal data. This demonstrates how AI now adapts to human behavior rather than forcing conformity to technology.
Pervasive AI Integration and Investment
AI has transitioned from competitive advantage to survival necessity. Over 90% of leading businesses continuously invest in AI, with three-quarters using it in at least one function. This widespread adoption occurs across automotive, healthcare, banking, and retail sectors. Intelligent capabilities are increasingly embedded directly into core applications. These applications include browsers.
Zero-Click Information Consumption
User behavior has fundamentally shifted toward conversational interfaces and direct AI answers. “Zero-click searches” are rising as AI chatbots drive 95-96% less referral traffic than traditional search. Users prefer immediate AI-generated answers. They choose ease over the effort needed to verify them. This accelerates reliance on AI agents over conventional browsing patterns.
Advancements in In-Browser AI Capabilities
JavaScript frameworks like TensorFlow.js and ONNX.js allow sophisticated AI processing directly within browsers. Compact Large Language Models can now operate locally. Multimodal AI expands capabilities beyond text. It includes vision and audio processing. Google AI Mode demonstrates advanced reasoning and multimodality, enabling deep research in minutes without constant server communication.
Microsoft’s new Copilot AI mode for Edge further enhances this with a modern homepage. It provides quick help as a browsing companion. It offers simple task handoff. Additionally, it has voice navigation and Copilot Vision for screen analysis and instant suggestions. It also includes multi-tab context evaluation. There is a Copilot-inspired theme and video summary. It offers AI tab grouping and Copilot Discover for tailored content. It also provides image generation and real-time video translation.
Growing Privacy and Security Concerns
Growing privacy concerns create demand for browsers prioritizing data protection. Many AI browser extensions collect personally identifiable information, with significant portions posing high cybersecurity risks. “Privacy by Design” principles like on-device processing become critical differentiators, minimizing external data transmission while maintaining AI functionality.
Difference between AI-powered browsers, Agentic AI browsers, and AI extension for browsers

AI-powered browser:
These are web browsers that integrate artificial intelligence capabilities directly into their core functionality to enhance the user’s browsing experience. Their primary goal is to make browsing faster, smarter, and more personalized.
Key features typically include AI-optimized search that understands user intent. They also offer one-click content summarization and writing assistance. Additionally, there are smart suggestions based on user tasks. The AI in these browsers works to adapt content dynamically to reading preferences. It filters information based on interests and simplifies workflows through predictive assistance. They transform the browser from a passive content container into a responsive companion.
Examples include Microsoft Edge with Copilot, Opera One with Aria, and Brave with Leo.
Agentic AI browser:
Agentic AI browser is a more advanced evolution where AI not only assists but also performs complex, multi-step tasks actively. It acts on behalf of the user, often autonomously. Agentic AI browsers are designed to interpret user commands. They translate user commands into actions. These actions include booking flights, filling out forms, or generating reports.
They move beyond simple search results to synthesize answers and automate entire workflows. Unlike traditional bots, AI agents can adapt their browsing patterns based on context. They retrieve content in real-time in response to queries. AI agents can even continue working offline in the cloud for complex tasks.
Opera Neon and Perplexity’s Comet are examples of browsers aiming for a full agentic AI experience. In these browsers, AI is the fundamental interaction model rather than a supplementary feature.
AI extensions for browsers:
AI-powered extensions for browsers are add-on tools. They integrate specific AI functionalities into existing web browsers. These functionalities are not built into the browser’s core architecture from the start. They typically offer targeted AI assistance for particular tasks.
There are common examples of extensions for various AI tasks. These include real-time AI-generated responses (like ChatGPT Chrome Extension). Other examples are writing assistance (Grammarly), content summarization (Glasp AI Summarizer), and data extraction (Browse AI).
While useful, they often “feel separate” from the core browsing experience. They may need manual triggers. They can be slower compared to built-in AI features. They enhance specific aspects of browsing. Still, they don’t fundamentally redefine the entire interaction model like a native AI browser or Agentic AI browser aims to.
Best AI browsers to track and try out
| Browser Name | Key AI Features |
| Microsoft Edge (Copilot) | Microsoft Edge browser offers deep integration with Microsoft 365. This enables instant content summarization and comprehensive writing assistance for emails and documents. Its AI-powered search optimizes queries for AI understanding. It includes features like a scareware blocker and an AI theme generator. It also provides automatic tab organization, text prediction, and translation capabilities. Edge is particularly well-suited for users already embedded within the Microsoft ecosystem. Learn more: Microsoft Edge — AI-Powered Browser |
| Opera One (Aria and Neon) | Opera One features the Aria assistant, which uses ChatGPT to give real-time answers. It boasts smart tab grouping through “Tab Islands” and multi-pane layouts for efficient multitasking. The browser also integrates social media and messaging directly, along with a built-in VPN and ad blocker. Its privacy-focused translation is powered by Lingvanex. It processes data on European servers to avoid third-party sharing. Opera One is designed for creators, multitaskers, and privacy-focused users wanting to adhere to EU data processing policies. Opera is also coming up with Opera Neon — an Agentic AI Browser. This will take actions on your searches and tasks. Learn more: Opera Aria — AI-Powered Browser |
| Arc Browser (Arc Max, Dia) | Arc distinguishes itself with an innovative sidebar interface and “Spaces” for organizing tabs and projects. Its “Arc Max” bundle includes AI-powered features. These features include “Ask on Page” for instant answers and 5-second link previews. It also automates tidying of tab titles and downloads. Additionally, users have direct ChatGPT access in the command bar. Arc also offers “Instant Links” and a “Call Arc” feature for spoken AI conversations. The Browser Company, the developer of Arc, is strategically shifting its focus towards its new Agentic AI Browser — Dia. It centers AI as the fundamental interaction model, moving beyond mere automation. Learn more: Arc Max — AI-Powered Browser |
| Perplexity AI (Comet) | Perplexity’s Comet browser aims to transform browsing into an “answer engine” with agentic search capabilities. It includes dynamic features like voice recognition, AI-driven search predictions, and enhanced privacy controls. Comet can also do tasks like checking shopping carts for discounts and sifting through unanswered emails. It even offers a “Try on” feature for clothing. The browser is envisioned as a “containerized operating system” for AI agents. Learn more: Perplexity Comet — Agentic AI Browser |
| Brave (Leo) | Brave’s AI assistant, Leo, offers AI chat without needing sign-in or data tracking, prioritizing user privacy. It is designed to be a secure and anonymous tool. This tool allows users to interact with any webpage, document, or PDF. They can do this without leaving the current page. It provides real-time summaries and translations and is tightly integrated with Brave Search. Users can opt for premium models. Alternatively, they may “Bring Your Own Model” (BYOM). This is done by connecting their own API endpoints or locally-running models. The free version does not need an account or login. It provides access to models from Mixtral. Access is also available to Anthropic’s Claude and Meta’s Llama. There is also a premium plan for faster responses and access to more models. Learn more: Brave Leo AI Assistant |
| SigmaOS Browser | SigmaOS is an AI browser backed by YCombinator. It is designed for founders, researchers, and content creators who want to be more productive and work faster on the web. The browser aims to be the “new home for your internet” by eliminating the chaos of countless tabs and distractions. It provides a focused environment for online work. SigmaOS AI browser features a built-in GPT, allowing for custom prompts and integrated tools for content creation. It enables users to save sessions, organize tabs, and visually develop ideas. Sigma AI Browser is positioned as a “thinking environment for working with AI,” particularly appealing to creators. Learn more: SigmaOS — AI Browser |
| Mozilla Firefox | Firefox has integrated AI capabilities through a dedicated sidebar shortcut. This shortcut provides access to a broader range of AI chatbots. These include Claude, ChatGPT, Gemini, Mistral, and HuggingChat. Its AI chatbots can interact contextually with selected text. They do not directly access the content of the current page. Learn more: Mozilla Firebox AI Chatbots |
| Fellou AI | Fellou AI “agentic browser” is designed to be an intelligent companion. It reads, acts, and manages workflows. It blends deep search and automation directly into the web experience. Key features include “Deep Search” with parallel queries across multiple platforms (e.g., Quora, X, academic sites) to create summarized reports, hands-free automation of routine tasks (e.g., drafting emails, posting to LinkedIn), and “Browser Content-Aware Automation” that understands the context of a webpage. It also supports “Shadow Workflows” that run in the background and local file automation. The architecture prioritizes privacy with local processing. Fellou claims to be significantly faster than competitors. It completes complex tasks in under 4 minutes, compared to 11 to 18 minutes for others like Perplexity. Learn more: Fellou AI Browser |
| Sigma AI browser | Sigma AI Browser is an AI-first browser built on a Chromium foundation. It is more than just a window to the internet. It acts as a personal AI agent with integrated tools. It incorporates an AI agent (SigmaGPT) to help users via deep-research workspaces and a privacy-first design. These features help users navigate, create, and automate tasks on the web. It’s a comprehensive AI toolkit that includes features like summarizing articles, generating content, and a writing assistant. To make certain of privacy and security, it uses end-to-end encryption for AI Chat conversations. The browser also implements encrypted DNS and phishing protection. Furthermore, it complies with GDPR and CCPA. The browser is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux. Learn more: Sigma AI-first Browser |
AI Browsers: Market Analysis
The AI browser market is one of the spaces where AI companies will target to change user behaviors. This will lead to a significant change in market share — a market war worth watching from 2025.
Major Sources used for this report’s section: Precedence Research, Coherent Market Insights, SP Global Market Intelligence, AInvest
AI Browser Market Snapshot
This snapshot table provides a high-level overview of the market’s current state and projected growth:
| Metric | Value (2025) | Value (Projection) | CAGR (Period) |
| Global AI Market Size | USD 757.58 Billion | USD 3,680.47 Billion (2034) | 19.20% (2025-2034) |
| Global AI Search Engines Market Size | USD 43.63 Billion | USD 108.88 Billion (2032) | 14% (2025-2032) |
| Generative AI Market Revenue | USD 16 Billion (2024) | USD 85 Billion (2029) | 40% (2024-2029) |
| AI SEO Tools Market | USD 1.2 Billion (2024) | USD 4.5 Billion (2033) | N/A |
| AI Content Market | USD 11 Billion (2025) | N/A | N/A |
| AI Search Engines Market Share (Web Search) | 61.7% | N/A | N/A |
| AI Search Engines Market Share (Generative AI) | 54.2% | N/A | N/A |
| AI Search Engines Market Share (North America) | 41.4% | N/A | N/A |
| AI Search Engines Market Share (Asia Pacific) | 19.3% | N/A | Fastest Growing |
Note: Data from. Projections and CAGR vary by specific market segment.
TAM / SAM / SOM estimates for AI browsers market
Understanding the Total Addressable Market (TAM), Serviceable Available Market (SAM), and Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM) is crucial for assessing the realistic market opportunity for AI browsers.
Total Addressable Market (TAM):
TAM is the broadest market for AI applications, encompassing all potential revenue if 100% of the market is captured.
The global AI market size is projected at USD 757.58 billion in 2025, with a forecast to reach approximately USD 3,680.47 billion by 2034. More specifically, the global AI Search Engines Market is expected to be valued at USD 43.63 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow to USD 108.88 billion by 2032. These figures represent the utmost theoretical revenue for AI-powered solutions, including AI browsers.
Serviceable Available Market (SAM):
SAM means the segment of the TAM that a business can realistically target and serve. It accounts for limitations like geographical reach or specific product specializations.
Given North America’s leading share in the AI search engines market (41.4% in 2025) and Asia Pacific’s projected fastest growth (19.3% in 2025), these regions offer significant SAM opportunities for AI browser developers. Furthermore, the existing browser market is dominated by Chrome with a 65% market share. Edge holds a 13% market share, and Safari holds 7% as of May 2025. This situation defines a large pre-existing user base. AI browsers can target this base for adoption.
Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM):
SOM is the specific part of the SAM that a business can realistically capture in the short to medium term. This consideration takes into account current resources, competitive landscape, and brand awareness.
The SOM for an AI browser would depend heavily on its unique features, target niche, and go-to-market strategy.
The overall AI market is undeniably massive. Still, the specific “AI browser” segment forms a subset. It primarily falls under the broader categories of “AI Search Engines” and “Generative AI” applications.
The considerable market figures suggest significant opportunities, but also imply intense competition. The practical challenge for new entrants lies in defining a defensible SOM within this rapidly evolving landscape. This might involve niching down or offering unique value propositions. A highly specialized approach can carve out a more manageable and attainable market share.
CAGR for AI browsers market
The growth trajectory of the AI browser market is reflected in the impressive Compound Annual Growth Rates (CAGR) across related AI segments:
- The Global AI Search Engines Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14% from 2025 to 2032.
- The aggregate revenue for the generative AI market is projected to grow at a significantly higher 40% CAGR from 2024 to 2029.
- The overall Artificial Intelligence (AI) market is forecasted to accelerate at a CAGR of 19.20% from 2025 to 2034.
- The code-generation sector is a key application area for AI in browsers. It is projected to show the fastest growth. This growth includes a CAGR of 53% from 2024 to 2029.
The higher CAGR observed for generative AI and code generation is greater than that of the broader AI search market. This suggests that AI browsers with advanced generative capabilities are positioned for more explosive growth.
This includes features like content creation, automated report generation, or complex task automation.
For example, the 53% CAGR for code generation significantly outpaces the 14% for AI Search Engines. This indicates that AI browsers are moving beyond simple search summarization. They offer robust generative features, like Dia’s content drafting. Opera Neon’s ability to create games and websites also plays a significant role. These innovations are tapping into the fastest-growing segments of the AI market. This implies where the most considerable revenue acceleration is expected in the coming years.
Projections for AI browser market
Market projections underscore the significant anticipated expansion across AI-related sectors:
- The Global AI Search Engines Market is projected to reach USD 108.88 billion by 2032, up from USD 43.63 billion in 2025.
- The Generative AI Market is estimated at $16 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to $85 billion by 2029.
- The overall Artificial Intelligence (AI) market is forecasted to reach approximately USD 3,680.47 billion by 2034, from USD 757.58 billion in 2025.
- The AI SEO Tools Market is projected to grow from $1.2 billion in 2024 to $4.5 billion by 2033, driven by demand for data-driven strategies and automation.
- Google’s AI Overviews, which offer AI-generated summaries directly in search results, are rapidly increasing in prevalence, appearing in 13.14% of all queries in March 2025, a significant jump from 6.49% in January 2025. They are projected to appear in roughly 30% of all Google searches by early 2025. [Source: SEMRush]
Market gaps and opportunities in the AI browsers space

Despite the rapid growth and increasing competition, significant market gaps and opportunities persist within the AI browser space.
Underserved user segments
Today, the mainstream browsers integrate general AI features. As a result, there are significant opportunities in developing highly specialized AI features. Vertical-specific AI browsers can cater to the unmet needs of niche professional segments.
We have covered about Vertical AI Agents to understand this more:
- Specific Professional Niches: There is a demand for highly precise, context-aware web automation and data extraction tools tailored for professionals. This includes investors and VCs who track financial market movements. Recruiters watch job listings across multiple platforms. Real estate agents extract property details for investment opportunities.
- Deep Work Environments: Users seeking less cluttered environments for focused work, with advanced organization capabilities, represent an opportunity. Examples include Arc’s “Spaces” feature and SigmaOS Browser’s positioning as a “thinking environment”.
- Privacy-Conscious Users: A growing segment demands on-device AI processing and zero data tracking. They seek browsers that focus on privacy over data collection.
- Creators and Visual Thinkers: This segment requires integrated tools for content creation. They need visual organization and multi-pane layouts to streamline their workflows.
- Industry-Specific Solutions (Vertical AI): Businesses in sectors with unique challenges can gain from tailored AI solutions. They may face stringent regulations or have specialized workflows. Vertical AI, designed with deep domain knowledge, offers regulatory alignment and streamlined integration, addressing needs that horizontal AI may overlook.
UI/UX gaps in current players
The evolving interaction paradigm with AI agents requires a redesign of browser UI/UX. This redesign aims to accommodate machine readability and enhance human-AI collaboration.
- Human-Centric Design Limitations: Traditional browser UI/UX is primarily designed for human users, often neglecting the distinct needs of AI agents. This leads to inadequate information architecture and insufficient APIs for seamless AI integration and data extraction.
- Data Structure Inconsistencies: The lack of standardized data structures and inconsistent metadata on websites presents a challenge for AI agents. It is difficult for them to understand the context and relationships between different pieces of information. This issue hinders automated tasks.
- Need for Context-Aware Interfaces: There is a clear need for dynamic UI elements. These include adaptive menus and task-specific toolbars. They can adjust based on the AI agent’s intent or the user’s current task.
- Efficient Data Processing: AI agents need streamlined interfaces. These interfaces must efficiently process and show large volumes of data at high speeds. They should reduce visual or interactive elements that might hinder performance.
- Security and Privacy Protocols: Ensuring robust security and privacy protocols for AI agents handling sensitive data is paramount. Traditional browser security models may not suffice for AI-driven interactions.
- Blending AI with Human Touch: A significant challenge lies in effectively blending AI capabilities with human support. Over-automation or a lack of human touch can lead to poor user experiences. This emphasizes the need for real-time feedback. It also highlights the importance of emotional connection in AI-driven designs.
Use cases no one is tackling (Yet)
The ultimate potential of AI browsers lies in achieving truly autonomous and undetectable web agents. These agents can execute complex, human-like interactions at scale. They can overcome current technical and anti-bot limitations.
- Reliable Autonomous Agents: The “holy grail” remains AI agent browsers that are fully reliable, scalable, and undetectable. They can execute complex, multi-step web tasks without being blocked by anti-bot defenses. These defenses include CAPTCHAs, fingerprinting, and user behavioral analysis.
- Seamless Proxy Integration: Solutions offer built-in proxy integration. This integration is across millions of high-quality residential IPs. It helps avoid IP bans and geo-restrictions for AI agents.
- Advanced Content Filtering & Tab Management: AI-powered tools genuinely reduce cognitive load. They achieve this by intelligently filtering content and managing tabs based on user preferences and context.
- Multimodal AI Extensions: Vision-enabled extensions can understand and process images directly in the page context. They also have audio processing capabilities for voice commands and transcription. This functionality does not rely on external services.
- Predictive Execution: AI systems can start likely operations. They can also pre-load content before explicit user requests. This creates a truly seamless browsing experience.
- “Vibe Coding” for Consumers: AI-powered tools that allow non-developers to generate code using natural language. This expands the user base for programming tasks.
Pricing pain points left unresolved
Addressing pricing transparency and flexibility is crucial for broader AI browser adoption. This is especially true for smaller users and startups. High and unpredictable costs can be a significant barrier.
- High Computational Costs: The significant computational costs and infrastructure requirements linked to training and running large AI models is challenging. These factors influence pricing.
- Lack of Transparency: Many current AI pricing models, particularly usage-based ones, lack transparency. This makes it difficult for users to predict and manage their expenses effectively.
- Expensive Solutions for SMBs: Some AI tools are prohibitively expensive for small teams and companies, limiting their adoption.
- Misalignment of Costs and Value: Difficulty arises in aligning expenses directly with data volumes. This also applies to performance needs or desired outcomes. These challenges can lead to perceived poor value.
- Need for Flexible Models: A demand exists for more flexible pricing models. These include pay-as-you-go options, free credits for experimentation, and tiered plans that scale with user needs. These models encourage broader adoption and reduce early barriers.
AI browser market maturity analysis
The AI browser market is navigating a complex phase of rapid growth, intense competition, and incipient consolidation.
Is the space saturated, growing, or consolidating?
The AI browser space is now in a rapid growth phase.
It is characterized by intense innovation and competition. There are clear signals of impending consolidation as larger players seek to integrate AI capabilities. This implies a “land grab” scenario where market share and unique value propositions are critical for survival.
The market is highly competitive. Established players like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Opera compete for market share. New entrants like Perplexity, Arc, Dia, Brave, and SigmaOS are also in the race.
The broader generative AI market is competitive. This is indicated by a Herfindahl-Hirschman Index of 857. The market is experiencing an expansion in the number of vendors. It is also seeing increasing revenue from tier 2 startups. The market for AI content tools is projected for explosive growth. At the same time, the digital marketing landscape is described as “increasingly saturated”.
Consolidation is expected in the broader SaaS market in 2025. This is driven by AI adoption. Major tech companies are actively seeking to acquire service capabilities. The AI market is advancing through various maturity levels. It moves from beginning “Awareness” to a “Transformational” stage. Many organizations are still in the early phases of AI adoption.
New entrant success rate
The AI crawler landscape experienced notable changes from May 2024 to May 2025, with GPTBot increasing its market share from 5% to 30%, while Meta-ExternalAgent entered at 19%. In contrast, traditional leaders like Bytespider faced declines, with PerplexityBot seeing a remarkable 157,490% rise in requests [Source: Cloudflare]
Despite this growth, only 30-35% of agentic AI projects succeed in completing multi-step tasks. Gartner forecasts that over 40% will be canceled by 2027 due to high costs and unclear value. Meanwhile, Google’s AI Overviews are increasingly used, rising from 6.49% to 13.14% of all queries between January and March 2025.
For new entrants, success hinges on both innovation and robust execution. They need to tackle challenges like bot detection. Additionally, they must show clear value to compete with established players.
Is it better to niche down or build horizontally?
For AI browsers, adopting a hybrid strategy may be beneficial. It should combine a horizontal, general-purpose AI core with vertical-specific features or integrations. This approach may offer the most effective path to market penetration. It will also offer defensibility.
- Horizontal AI: Offers broad applicability across industries. It enables faster deployment with ready-to-use models and APIs. It provides cost efficiency through shared costs. It benefits from extensive vendor ecosystems and community support. Nonetheless, it often lacks deep industry specialization. Customization is required for specific contexts. There may be gaps in regulatory compliance for highly regulated sectors.
- Vertical AI: Designed for specific industries, these systems leverage deep domain knowledge and specialized datasets. They guarantee strong regulatory compliance, integrate well into existing processes, and excel at niche tasks. Nonetheless, they offer limited flexibility for other uses, usually need longer development times, and entail higher upfront costs.
Many businesses are adopting a mixed approach, using horizontal AI for general tasks while implementing vertical AI for industry-specific processes.
The trade-offs between horizontal and vertical AI show unique challenges. A horizontal strategy may struggle against dominant players like Chrome or Edge, while a vertical approach could limit market size. A hybrid model that offers broad AI capabilities—like summarization and writing assistance—alongside deep customization for specific workflows (e.g., legal, finance) could attract a wider audience and tackle niche pain points. This strategy aligns with “rewiring user’s daily motion” by enhancing existing professional workflows.
Potential business models and monetization strategies for AI browser products
Building browsers requires technical skill and commitment for long-term usage.
Now, mega-players like Google and Microsoft dominate the market. The rise of Generative AI opens opportunities for innovators like The Browser Company and Perplexity. Smaller players like Opera and Brave can experiment with Agentic AI Browsers.
AI browsers also offer various monetization opportunities, moving beyond traditional advertising to include direct use and advanced services.
Direct monetization models for AI browsers
- Subscription-based services: A prevalent model involves charging users recurring fees for access to advanced AI features, premium AI models (e.g., Perplexity Pro, Brave Premium models), enhanced privacy functionalities, or higher usage limits. This allows for a predictable revenue stream tied to value delivery.
- AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS): Providers offer AI models via API. This is used for automated data extraction or content generation. It is typically provided on a pay-per-use or credit basis. This model serves businesses and developers needing specific AI functionalities without building them from scratch.
- Value-based pricing for specialized solutions: Targeted AI browser tools for specific industries can command premium pricing. For instance, enterprise-grade web automation and specialized legal research tools offer significant value, justifying their costs.
- Dynamic Pricing: AI systems can be used to enhance pricing in real-time. This involves adjusting service costs based on fluctuating demand, competitive pricing, and individual user behavior, thereby maximizing revenue per transaction.
- Embedded AI Features (Freemium): A common strategy is to offer basic AI features for free. This attracts a large user base. Then, upsell to premium tiers that unlock more advanced capabilities, greater speed, or higher usage quotas.
Indirect monetization using AI browser capabilities
- Enhanced Customer Engagement and Personalization: AI enables hyper-personalized customer experiences. It uses tailored recommendations, driving higher conversion rates, improving satisfaction, and fostering loyalty, ultimately increasing revenue.
- Operational Efficiency & Cost Savings: AI browsers can automate repetitive tasks. This includes data entry, customer service interactions, and content creation workflows. This automation significantly reduces manual labor costs and enhances overall productivity for businesses, translating directly into financial savings.
- Data Monetization Through AI Insights: AI can analyze anonymized user data to detect trends and predict behaviors. It generates insights for targeted advertising or market intelligence, but requires careful navigation of privacy regulations.
- Content Monetization: AI browsers enhance content creation, optimization, and distribution for creators and publishers. This leads to increased ad revenue and higher subscription rates. For example, Brave’s Basic Attention Token (BAT) enables users to earn cryptocurrency by viewing privacy-preserving ads. BAT can further be used to tip creators or exchanged for other currencies.
The shift from traditional ad-based monetization to subscription models reflects a growing market appreciation for direct utility and privacy. AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS) illustrates this trend, with increasing demand for enhanced capabilities alongside privacy.
Browsers like Chrome and Edge have depended on advertising. In contrast, AI-focused browsers like Perplexity and Brave are adopting subscription or token systems. They value privacy as a key feature. This indicates that AI functions are becoming essential to the browsing experience. Users are willing to pay for improved productivity and data protection.
AI browser developers face the challenge of balancing data needs for AI personalization with user privacy expectations. They must do this under heightened regulatory scrutiny. Companies that effectively communicate and deliver clear value in terms of time savings and efficiency will have a competitive edge.
AI browsers – VC sentiment and deal activity landscape

Venture Capital (VC) sentiment towards AI browsers and the broader AI market remains highly positive. This marked by significant deal activity and a strategic shift in investment focus:
Recent fundraising rounds for AI browsers
The past year has seen significant funding rounds for companies in the AI browser and agentic AI space, indicating strong investor confidence:
Perplexity AI funding
This AI search engine has raised a total of $1.02 Billion across 8 funding rounds, with the latest being on Jul 18, 2025 for $100M. There was a Series C round for $500 million in December 2024. The lead investors were SoftBank, NVIDIA, and Jeff Bezos. Another Series C round in August 2024 secured $250 million. The investors were SoftBank Vision Fund, NVIDIA, and Jeff Bezos. Other investors included Andrej Karpathy, Yann LeCun, and Wayra. Perplexity’s valuation reached $9 billion as of December 2024.
The Browser Company (Arc/Dia):
The creator of the Arc browser has raised a total of $68 million. Its most recent funding was a $50 million Series B round in March 2024 led by Pace Capital. The funding valued the company at $550 million. Notable individual investors include Jeff Weiner, Ev Williams, Dylan Field, Akshay Kothari, and Jason Warner.
xAI (Elon Musk):
Elon Musk’s X AI reportedly closed a massive $10 billion in debt and equity funding. This includes $5 billion in strategic equity investment. The round occurred recently (June-July 2025).
Elon Musk’s xAI is developing a native Grok desktop app for Windows and Mac, moving beyond browser-based AI interactions. Musk said, “We can’t live in the browser forever.”
He aims to offer deeper system integration. He seeks local file access. Additionally, he wants offline functionality that web-based tools can’t give. This is part of his broader strategy. He wants to embed AI directly into daily computing infrastructure. He positions xAI to compete with desktop-integrated AI solutions from Apple and Microsoft.
Thinking Machines Lab (Mira Murati):
The AI startup was launched by former OpenAI CTO Mira Murati. It reportedly secured a $2 billion seed round. The startup was valued at $10 billion, with Andreessen Horowitz leading the investment (June 2025). Though not specified it, their website highlights working on building user-centric AI products, that may involve AI browsers – but that is just my hunch!
BrowserUse
Browser Use, a Y Combinator startup founded by Magnus Müller and Gregor Žunič, has raised $17 million in seed funding. It is led by Felicis to develop tools that help AI agents navigate websites more effectively. The company converts website elements into a “text-like” format. Agents can understand this format, which solves the problem of vision-based systems. These systems rely on screenshots and often break. This approach enables more reliable and cost-effective automation compared to traditional methods. Browser Use gained significant attention after its use in Butterfly Effect’s viral Manus tool. More than 20 companies in the current Y Combinator batch have adopted their solution. This positions it as a fundamental layer for the growing AI agents market.
BrowserBase
In June 2025, Browserbase secured a $40 million Series B round. Notable Capital led this round, with backing from CRV and Kleiner Perkins. The valuation was about $300 million. This nearly quadrupled its valuation from months earlier. This financing supports rapid growth after a $6.5 million seed round in June 2024. Additionally, there was a $21 million Series A in late 2024. These funds fueled team expansion and product innovation.
With the new capital, Browserbase launched Director. This is a no-code automation platform that complements its developer-focused Stagehand framework. It enables users to build browser automations through natural language prompts. This funding is a pivotal milestone. It helps to build Browserbase as a foundational infrastructure provider for AI agents. It also supports web automation at scale.
Sigma OS browser
London‑based SigmaOS, a Y Combinator–backed startup founded in 2021, secured a £3.4M (~$4 million) seed round in November 2022. This was led by LocalGlobe alongside YC, 7percent Ventures, Moonfire Ventures, and more.
The funding empowered a lean team of five to move beyond beta and launch SigmaOS 1.0—a CrOS‑based browser built around vertical workspaces, split‑screen multitasking, tab snoozing, and built‑in privacy and collaboration tools. With tens of thousands of users across 100+ countries, the company was already generating revenue. Around 30% convert to the $10/month subscription plan and growth is trending at about 40% month‑over‑month. This seed capital has since enabled feature expansion—especially AI enhancements. This includes contextual assistant Airis, “pinch‑to‑summarize,” link previews, and the “Look it up” summary tool. All these lead toward a browser experience that’s productivity‑first and AI‑powered.
Broader funding analysis for AI browsers
Recent funding rounds have been considerable, with Perplexity AI and The Browser Company standing out. These rounds show strong VC confidence in the AI browser sector. While BrowserUse and BrowserBase show optimism in the broader agentic AI space, despite the high failure rates of some early projects.
The significant capital injections reveal that venture capitalists are strategically investing in specific teams and deep technological approaches. Large seed rounds for xAI and Thinking Machines Lab highlight significant interest in foundational AI research. They also show a demand for large-scale models powering advanced AI browser capabilities. Investors are discerning, differentiating between superficial solutions and those with strong underlying technology, with a clear vision for AI-native experiences.
Top venture capitalists active in AI browser domain
Leading venture capital firms are actively investing across the AI stack, from foundational models to application layers like AI browsers:
- Sequoia Capital: Remains the top investor in AI and machine learning since 2023. Its extensive AI portfolio includes prominent names like OpenAI, xAI, and Glean (an enterprise AI search platform).
- Andreessen Horowitz (a16z): A key player in the AI space. A16z has backed major companies like OpenAI, xAI, Mistral, and Cursor. Cursor is an AI coding startup.
- Pioneer Fund: This fund uniquely focuses on Y Combinator startups. It operates a dedicated machine learning and AI fund. The focus is on investing in early-stage AI ventures.
- Khosla Ventures: Khosla Ventures was an early backer of OpenAI. It is a strong champion of AI. The firm has a particular focus on AI applications in medicine.
- SoftBank Vision Fund: A lead investor in Perplexity AI’s significant Series C rounds, demonstrating its commitment to large-scale AI applications.
- NVIDIA: NVIDIA has invested in Perplexity AI. Their involvement underscores the synergy between AI applications and the demand for its high-performance GPUs.
- Pace Capital: Led The Browser Company’s Series B funding round, indicating investment in innovative browser experiences.
- Y Combinator: An investor in Sigma OS, Y Combinator continues to be a crucial early-stage accelerator for many AI startups.
Shift in funding from AI wrappers to AI infrasructure or deep tech
The term “AI wrapper” describes companies that only build user interfaces atop existing AI models without adding significant proprietary value.
The venture capital funding landscape is shifting from simple “AI wrapper” solutions to AI infrastructure and deep technology. Sustainable competitive advantage now comes from proprietary models, unique datasets, or novel architectures rather than just integrating existing APIs. This raises the bar for AI browser startups to show genuine innovation.
Venture capitalists seek systems that transform human behavior patterns into investment signals. They are focusing on complex challenges and “hard to automate zones.”
Perplexity AI was initially viewed as an OpenAI/Bing “wrapper.” It has evolved to create its own search index. The company is developing its own Large Language Models (LLMs) using open-source models like Mistral-7b and Llama2-70b. Perplexity AI aims for deeper technological differentiation.
The AI browser market is a fiercely contested arena, with established tech giants and agile startups deploying diverse strategies to capture market share.
Key AI browsers competitive landscape
| Browser Name | Key AI Features | Positioning/Focus | Pricing Model | Funding Status (if available) | Revenue Status (if available) | Customer Support Channels | Tech Stack (if available) |
| Microsoft Edge (Copilot) | Deep MS 365 integration, summarization, writing assist, AI search, scareware blocker, tab organization, translation | Productivity, MS ecosystem integration, AI as core brain | Freemium (Copilot access, some features free) | Backed by Microsoft | N/A (part of Microsoft revenue) | Help Center, Docs, Community | Chromium-based |
| Opera One (Aria) | Aria assistant (ChatGPT/real-time answers), smart tab grouping, multi-pane layouts, privacy-focused translation | Creators, multitaskers, privacy, gaming (GX) | Freemium (Aria free, premium subscriptions for Neon) | Public company (NASDAQ: OPRA) | $481M (2024), $1B market cap (Aug 2024) | Help pages, FAQ, Community forums, Bug reports | Chromium-based, Multithreaded Compositor |
| Arc Browser (Arc Max, Dia) | “Ask on Page”, 5-sec previews, tidy tabs/downloads, ChatGPT in command bar, “Call Arc” (spoken AI) | Productivity, organization, unique UI, AI-first interaction (Dia) | Free (Arc Max opt-in) | $68M total, $550M valuation (Mar 2024) | N/A | Contact form, Help Center, Blog, FAQs | Chromium-based, Swift (macOS/Windows) |
| Perplexity AI (Comet) | Agentic search, voice recognition, AI search predictions, privacy controls, shopping/email parsing, “Try on” feature | Answer engine, agentic AI, challenging traditional search | Freemium ($20/mo Pro, $40/mo Enterprise Pro) | $915M total, $9B valuation (Dec 2024) | N/A | Discord, Email (support@perplexity.ai), Intercom (Pro) | Chromium-based, GPT-4 Turbo, Claude 3, proprietary models, Mistral, Llama2 |
| Brave (Leo) | AI chat (no sign-in/tracking), real-time summaries/translations, Brave Search integration, BYOM | Privacy-focused, crypto rewards (BAT), ad/tracker blocking | Free (Leo chat), Optional Premium models | $7M Seed (2016) | $2.63M (Dec 2023) | Community forums, GitHub, Help Center | Chromium-based, Meta Llama 3, Mistral/Mixtral |
| Sigma OS Browser | Built-in GPT, custom prompts, content creation tools, session saving, visual idea development | Thinking environment for creators | Free to Use | $125K Seed (Sep 2022) | N/A | Email (support@sigmabrowser.com) | N/A |
| Mozilla Firefox | Sidebar access to multiple AI chatbots (Claude, ChatGPT, Gemini, Mistral, HuggingChat), contextual text interaction | Privacy, open-source, user choice | Free | N/A | N/A | Help pages, Community forums | Gecko engine (core), WebExtensions |
The top AI browsing features offered by each
The feature sets across AI browsers are converging around core AI functionalities like summarization, writing assistance, and intelligent search. However, differentiation is emerging through unique UI/UX paradigms, strong privacy commitments, and specialized agentic capabilities.
Microsoft Edge (Copilot):
Offers deep integration with the Microsoft 365 ecosystem. It enables instant content summarization and AI-powered writing assistance. Additionally, it provides AI-optimized search. Extra features include a scareware blocker, an AI theme generator, and automatic tab organization.
Opera (Aria and Neon):
Features the Aria assistant, which integrates ChatGPT and provides real-time answers. It boasts innovative smart tab grouping (Tab Islands) and multi-pane layouts. Opera also includes a built-in VPN, ad blocker, and privacy-focused translation powered by Lingvanex.
“So on paper, it seems like Opera has taken this nugget of great tech in Browser Operator and turned it up to 11 by making a big bet on what the future of web browsing will actually be. It’s a bold take, and after testing the underlying tech myself a month ago, I do believe that an agentic assistant is core to the future of web browsing.”– Jason England on Tom’s Guide
Arc Browser (Arc Max, Dia):
Known for its innovative sidebar interface and “Spaces” for task organization. Arc Max integrates AI features like “Ask on Page” for instant answers. It provides 5-second link previews. It also offers automatic tidying of tab titles and downloads. It allows direct ChatGPT access from the command bar. It offers “Instant Links” and “Call Arc” for spoken AI conversations. Dia, the Browser Company’s new focus, centers AI as the fundamental interaction model.
“Dia removes friction, and that counts for something. It speeds up minor tasks and smooths out workflows, making the browser feel more like a helpful assistant than just a window to the web. However, I don’t see it replacing my go-to AI tools for serious work. For complex tasks, I still default to ChatGPT because it’s simply better at handling depth and nuance.”
– Vinit Nair on his Medium Review
Perplexity AI (Comet):
Transforms browsing into an “answer engine” with agentic search capabilities. Features include voice recognition and AI-driven search predictions. It also has enhanced privacy controls. The system can parse shopping carts for discounts. It can also dig up unanswered emails. It also offers a unique “Try on” feature for clothing.
Here’s a review by Dharmesh on Perplexity’s Comet:
“I’ve been testing Perplexity’s new AI-enhanced browser called Comet, and it’s the first time in years that I’ve genuinely considered switching away from Chrome. I’ve long said it would take something really special to get me to switch away from Chrome (old habits die hard). I’ve tried Arc, Brave, and others–they never stuck. (Yes, I’m playing around with Dia too — but nothing to report yet).
Comet might be the thing that finally gets me to switch for good. It’s the first browser that makes browsing feel genuinely different for the first time in over a decade.”
— Dharmesh Shah, Founder and CEO at HubSpot, in his Simple.AI newsletter
Brave (Leo):
Prioritizes privacy with AI chat that requires no sign-in or data tracking. It provides real-time summaries and translations. It is tightly integrated with Brave Search. Users can “Bring Your Own Model” (BYOM) for custom AI integration or use optional premium models. It can also translate between languages and offer coding assistance with suggested and sample code.
Its core features emphasize privacy and security. Chats are not retained, shared, or used for model training. No account or login is required for the free version.
The free version provides access to models from Mixtral, Anthropic’s Claude, and Meta’s Llama. Users can also use their own models through the “Bring Your Own Model” (BYOM) feature. For convenience, chats can be stored locally on the user’s device. You can access them later through the Leo full-page view or the browser sidebar.
Note: I could not find a dedicated review on Brave’s Leo feature. However, I found a Leo Roadmap on brave’s website that mentions many upcoming updates. This includes support for handling content across multiple tabs and image analysis (vision support). They are developing agentic AI that can act on your behalf while maintaining strong privacy safeguards. Brave is also working on on-device AI for offline use. They plan to introduce richer outputs, task scheduling, and audio responses, all with a privacy-first approach.
Learn more: Brave Leo 2025 updates
SigmaOS AI Browser:
SigmaOS is built on a WebKit foundation and is compatible with some Chrome and Firefox extensions, as well as password managers like 1Password. Key features focus on enhancing productivity and organization. It offers a unique user interface with vertical tabs, which users can organize into “workspaces”. This helps manage different contexts of work or personal life. This approach allows for a clutter-free and highly focused browsing experience, moving all work into a single window.
The browser also includes a “focus mode” and a “tagging” system. This allows users to group bookmarks into categories for better organization and searchability. Furthermore, its workspaces can be shared for collaborative projects with other users. By enabling a “WebKit+” setting, users can also significantly improve the browser’s performance and speed.
I started using the browser not so long ago and I can say it’s one of my favorites (along with zen browser). At first the learning curve was bigger but once I got used to the shortcuts my experience was really smooth. I like the idea of marking the pages as done. Also the tagging is a great feature.
The browser is lightweight and fast once you allow using WebKit+
Of course there is no such thing as a perfect browser and they can improve some things. Also, I would prefer more information about upcoming features and better communication from the developers. But overall my experience is great.
That being said I can understand this browser is not for everybody’s taste and the lack of windows and Linux compatibility is a huge factor. But I also agree the hate towards it being a bit too much.
– Alexa-6 on Reddit about SigmaOS Browser
Mozilla Firefox:
Provides a dedicated sidebar shortcut for accessing a broad range of AI chatbots. You can access chatbots like Claude, ChatGPT, Gemini, Mistral, and HuggingChat. It supports contextual text interaction, though direct page content access by AI is limited.
They had launched ‘Orbit’ AI Assistant — but that is stopped since June 26, 2025.
Fellou AI browser
Fellou AI is an “agentic browser.” It acts as a digital companion. It manages a user’s workflow directly within the web experience. Its key feature, “Deep Search,” performs parallel queries across platforms like X, Quora, and academic sites to generate summarized reports. The browser allows “hands-free” automation for tasks like drafting emails and posting on LinkedIn with simple instructions. It includes “Browser Content-Aware Automation” to understand webpage context. It also includes “Shadow Workflows” that run tasks in the background without disrupting the user. The company claims its approach enables faster completion of multi-domain tasks. It finishes workflows in under four minutes. This is compared to 11 to 18 minutes for other tools. It also supports local file automation and ensures data security with a privacy-first architecture.
The report generation is really impressive. I was also blown away by how comprehensive the outputs are – definitely seems like it’s not limited by tokens like regular AI. The deep search capability is no joke.
When performing a deep search, Fellou simultaneously opens multiple subwindows, extracting or summarizing information from each. It collects and processes information from multiple sources simultaneously, typically compiling this information into a report.
For report creation, Fellou generates actual code to construct a webpage for browser display.
The reports produced are remarkably detailed and comprehensive — far more extensive than what typical AI tools could generate given token limits. The content is thorough and high-quality.
Sigma AI browser
The Sigma AI Browser features a complete AI Toolkit at its core, enabling users to ask, write, and summarize content.
The AI chat agent, SigmaGPT, can summarize pages, write or translate text. It can generate various types of content like social media posts and SEO content. The browser features an Intelligent Browse function with an AI assistant for content generation and instant summaries. Its Writing Assistant helps with suggestions and rephrasing. A Password Manager safely creates and autofills strong passwords. For security, it employs end-to-end encryption, encrypted DNS, and phishing protection. It is also GDPR and CCPA compliant with no user tracking for ads. Future updates will bring an autonomous AI agent for routine tasks and a Deep Research tool for citation-rich insights.
Note: I could not find reviews or YouTube videos available on Sigma AI browser.
AI browser positioning analysis
The competitive landscape is characterized by a “Browser Wars 2.0.” The primary battle is for “who owns the layer of intelligence inside” the browser. This is more significant than merely owning the window to the internet.
- Microsoft Edge: Leverages its deep integration with the Windows operating system and the Microsoft 365 ecosystem. It positions Copilot as the central AI brain, aiming to enhance productivity across all user activities.
- Opera: It differentiates itself through innovative tab management features like “Tab Islands.” It has robust built-in privacy tools like a VPN and ad blocker. Opera strategically focuses on niche user segments, particularly gamers with Opera GX and creative professionals with Opera One. Opera Neon signifies an ambitious move towards a full “agentic AI” experience.
- The Browser Company: It positions itself as an “operating system for the web”. The interface is distinctive and sidebar-centric. It emphasizes productivity, organization, and a clutter-free experience. Its new browser, Dia, signifies a radical pivot, centering AI as the fundamental interaction model rather than a supplementary feature.
- Perplexity AI: It positions itself as an “answer engine” and “agentic search” platform. It directly challenges traditional search engines by providing direct, cited answers. It also automates complex tasks. Its Comet browser aims to be a “containerized operating system” for AI agents.
- Brave: Maintains a strong focus on user privacy. It offers aggressive ad and tracker blocking. There is no data tracking for its AI chat (Leo). The browser also features a unique cryptocurrency-based rewards system (BAT). It integrates its own privacy-first search engine.
- Google Chrome: Despite its dominant market share (65%), Chrome is integrating Gemini with new features. These features include “Help me write,” AI-powered tab organization, and summarization. “Project Mariner” explores autonomous agents. Nonetheless, its massive existing user base constrains radical innovation. Alienating millions of users is not a choice.
- SigmaOS: A browser designed for “productivity nerds,” specifically founders, researchers, and content creators. Its core positioning is to manage information overload. It provides a streamlined, organized workspace that turns tabs into tasks. This approach makes users faster and more productive on the web.
- Sigma AI Browser: This browser is positioned as an AI-first tool for deep research, content creation, and workflow automation. It aims to offer a new experience for founders and researchers. It offers an autonomous AI agent that can plan, execute, and report on complex tasks.
- Fellou AI: Positions itself as a “new digital co-worker” and an “agentic browser” that acts autonomously to manage entire workflows. It differentiates itself by focusing on the seamless automation of multi-step tasks. It uses plain-English instructions and a “content-aware” understanding of web pages. This approach, it claims, reduces manual intervention by up to 94% compared to traditional browsing.
The competitive landscape is evolving into a “Browser Wars 2.0,” where the focus is shifting from controlling internet access to owning the embedded intelligence layer. Merely having AI features is not enough; the key differentiator is how these features transform user interactions with the web. For example, Dia’s AI-as-core model and Perplexity’s answer engine illustrate this shift. This suggests that user stickiness and loyalty will increasingly stem from integrated AI that redefines the user’s digital workflow.
AI browser pricing analysis
The pricing strategies in the AI browser market largely show a move towards subscription models for premium AI capabilities. This indicates a growing willingness among users to pay for enhanced features and utility.
Perplexity Comet Pricing

Offers a free tier for basic usage. Advanced features and multimodal capabilities are available through a Pro subscription plan priced at $20/month. An Enterprise Pro version tailored for businesses is available at $40/month or $400/year for companies with fewer than 250 employees. For Comet AI browser, they have mentioned that a free version will be inlcuded with Perplexity. At the time of publishing this AI browsers report, Comet is available to Perplexity Max subscribers. It is also available to select Perplexity Pro subscribers and by invitation.
Microsoft Copilot Pricing

It is free to use Microsoft Copilot on web and mobile for browsing using Microsoft Edge browser. If you need more features of Copilot, explore its paid plan starting at USD 25/user/month or INR 2000/user/month – learn more
Browser Copilot:

Browser Copilot AI provides access to a suite of AI models, including Claude 3.7 Sonnet, ChatGPT-4o, Gemini 2.0, Llama 3.3, and Perplexity, each valued at $20/month. This suggests a bundled value proposition for access to multiple leading AI models.
Browse AI:

Browse AI offers a freemium model with a Free plan that provides 50 credits per month. The paid plans include Personal, which costs $19/month and is billed annually, providing 12,000 credits per year. The Professional plan costs $69/month, billed annually, and offers 60,000 credits per year. A Premium plan with customized pricing starts at $500/month, billed annually, with credits starting from 600,000 per year.
Opera Neon:

Opera’s Neon Agentic AI browser is currently at a waitlist at the time of publishing this report.
OpenAI (underlying model):
It offers a free tier for casual exploration. There is a Plus plan for frequent users at $20/month. API tiers are based on token usage for scalable, high-volume tasks.
I have included OpenAI here because they are also working on releasing their own OpenAI Agentic AI browser. They will offer a fully integrated AI assistant that can pull data from open tabs to give more contextual responses. It is expected to include features like AI summaries of articles, videos, and PDFs. It will also support for images, voice, and files. The browser may also intelligently complete forms and schedule tasks based on user intent, leveraging advanced capabilities seen in GPT-4o. By owning the browser, OpenAI will gain access to extensive user behavior and data, like Google’s approach with Chrome.
Brave (Leo)

Brave offers a free version with its AI chat (Leo), with optional premium models available.
Leo AI, the intelligent assistant built into the Brave browser, can be accessed through a Premium subscription priced at $14.99 per month or $149.99 per year. The subscription includes higher usage limits, access to top-tier AI models, and early access to new features. Users can also take advantage of a 7-day free trial before committing to a plan.
SigmaOS AI browser

SigmaOS provides a free browser experience for all users, making it easy to get started without any upfront cost. For those interested in enhanced AI-powered features, SigmaOS offers paid plans. The $20/month tier increases rate limits for AI features. The $30/month tier unlocks unlimited usage and lets users choose between advanced AI models like GPT-4, Perplexity, and Claude 3 Haiku.
The company has shifted its monetization strategy to focus on these AI features, moving away from team-based pricing. This approach allows users to access basic AI tools for free, with premium options available for power users.
Fellou AI:

This browser is currently in an early adopter/beta phase, offering free access to its full feature set. The company plans to adopt a freemium model upon its official launch. In this model, basic browsing will stay free. More advanced features, like automation, “Shadow Workflows”, and enterprise-level API usage, will be available in premium tiers.
Sigma AI Browser:
A public pricing model has not yet been announced as it is in active development and is available for waitlist. As per their website, they have mentioned August 2025 for release. However, it is still not available at the time of publishing this report.
AI browser pricing trends

The pricing of $20-$40 per month for premium AI browser features suggests a value benchmark. While access to underlying AI models reflects advanced capabilities. The freemium model, offering basic features for free, attracts users before converting them to paid subscriptions. Browse AI’s pay-as-you-go model emphasizes utility and task completion. This indicates AI browser companies must define their value proposition to justify fees. They must highlighting the benefits and efficiencies their features offer.
Potential customer segments for AI Browsers
Let’s explore the potential customers who would want to adopt using AI browsers:
General web users
- Pain Points: These users often experience information overload, a desire for faster and smarter browsing, a need for content clarity (e.g., summaries), challenges with efficient multitasking, and growing concerns about online privacy.
- Buyer Decision Criteria: Key factors influencing their choice include overall speed, privacy features, and ease of use. Personalization capabilities and seamless integration with their daily online tasks are also important.
- AI Browser Appeal: AI browsers attract this segment through built-in AI assistants. They offer one-click content summarization and integrated writing tools. Additionally, they give smart suggestions and an all-in-one workspace. This reduces tab switching and clutter.
Professional or knowledge workers
This segment includes researchers, marketers, developers, analysts, and investors who leverage the web extensively for their work.
- Pain Points: Professionals face tedious manual data entry and scraping. They deal with time-consuming research and the need for complex pattern recognition. There are demands for workflow automation and efficiency in content creation. Additionally, staying updated on rapidly evolving industry trends is a challenge.
- Buyer Decision Criteria: Their decisions are driven by productivity enhancement and robust automation capabilities. They are influenced by the accuracy of AI-generated insights and seamless integration with existing professional tools (via APIs). Additionally, they consider the ability to handle complex multi-step workflows and the reliability of data extraction.
- AI Browser Appeal: AI browsers offer automated data extraction and streamlined form filling. They allow continuous website monitoring and enhanced lead generation. They also enable efficient content creation and optimization. Additionally, AI browsers give advanced market research capabilities and “vibe coding” for non-developers.
Privacy-conscious users
- Pain Points: This segment is particularly concerned about data tracking by traditional browsers and advertising networks. They are also worried about extensive personal data collection. Additionally, this segment desires a more anonymous browsing experience.
- Buyer Decision Criteria: Their primary criteria are strong privacy features. These include aggressive ad and tracker blocking, built-in VPNs, and on-device data processing. There are also explicit policies on zero data retention and anonymization. Transparency in data handling is also crucial.
- AI Browser Appeal: Browsers like Brave’s Leo offer a no-sign-in and no-data-tracking AI chat. Opera focuses on privacy with its translation feature. Dia emphasizes local context handling. These features strongly appeal to this segment.
Creators, designers or other multi-taskers
- Pain Points: These users struggle with tab clutter. They have difficulty managing multiple concurrent projects. There is a need for visual organization. Efficient content drafting and rewriting are challenging. They need seamless cross-application data transfer.
- Buyer Decision Criteria: They focus on innovative tab management systems and split-screen viewing capabilities. They also value integrated writing and design tools. Additionally, robust visual organization features and extensive customization options are important to them.
- AI Browser Appeal: AI browsers like Arc have features like “Spaces” and a sidebar. Opera offers “Tab Islands” and multi-pane layouts. Sigma AI Browser is positioned as a “thinking environment.” These browsers cater specifically to these needs.
Enterprises or businesses
- Pain Points: Enterprises face challenges in scaling AI adoption across their organization. They struggle with integrating AI into complex existing systems. Ensuring data security and regulatory compliance is challenging. Achieving measurable ROI from AI investments is another issue. Lastly, automating customer service at scale is a concern.
- Buyer Decision Criteria: Key decision factors include scalability and robust security measures. Compliance with industry regulations is essential. There must be strong integration capabilities with existing enterprise software. The vendor should have a proven track record of ROI. Vendor skill and reliable customer support are also crucial.
- AI Browser Appeal: AI browsers appeal to enterprises through agentic AI capabilities for workflow automation. They will use AI-powered customer service chatbots and advanced data analytics. These analytics lead to actionable insights. Additionally, there is the potential for customized AI solutions tailored to specific business needs.
The diverse range of customer segments and their distinct pain points underlines the necessity for AI browsers to either specialize in a specific segment. They could also offer highly customizable features for multiple user personas. A privacy-conscious user concerned about data tracking will have different needs. These needs differ from a professional seeking automation for market research. This highlights the strategic debate around niching down versus horizontal expansion. It indicates that successful AI browsers will need strong user segmentation. They will also need a tailored product development roadmap to meet these varied demands.
Buyer decision criteria for AI browsers
The decision to adopt an AI browser is influenced by a complex mix of functional, performance, and strategic criteria. Beyond core functionality, buyer decisions are driven by trust across privacy, reliability, and ethics). The browser’s ability to integrate into existing workflows also matters. Hence, “responsible AI” and “design for human-AI collaboration” are critical differentiators.
Functional and performance criteria
- AI Capabilities: The breadth and depth of integrated AI features are paramount. They include summarization, content generation, task automation, and intelligent search. The accuracy of AI outputs and the ability to understand complex queries and user intent are also critical.
- Speed and Efficiency: Users value fast loading times and smooth overall performance. They value real-time AI processing. Predictive loading capabilities that predict user actions are also essential.
- Integration: Seamless integration with existing web standards, third-party applications, and current user workflows is essential. This approach helps to avoid friction and maximize utility.
- Customization: The ability to personalize the AI assistant’s style is important. Customizing the UI layout and managing tabs effectively are also crucial. Adapting to individual user preferences significantly enhances the user experience.
- Usability/UX: An intuitive interface, ease of use, minimal cognitive load, and effective tab management contribute to a positive user experience.
- Scalability: For both individual power users and enterprises, the AI browser’s ability to handle increasing data volumes is crucial. It must manage complex tasks without experiencing performance degradation.
Non-functional and strategic criteria
- Privacy and Security: This is a critical concern, particularly as AI agents handle sensitive user data. Buyers examine robust data protection measures. They consider on-device processing capabilities. They evaluate minimal data collection practices and strong encryption. Compliance with relevant regulations like GDPR and CCPA is also scrutinized.
- Trust and Reliability: Users need assurance about the transparency of AI’s decision-making processes. They need the citation of sources for AI-generated information. It is important to have the ability to mitigate hallucinations. Additionally, consistent and dependable performance is essential.
- Cost and Value: Clear and predictable pricing models are significant factors. These models can be tiered or usage-based. The perceived value for money and the demonstrable return on investment (ROI) for businesses also play a crucial role. Trials and pay-as-you-go options can reduce adoption barriers.
- Vendor Skill and Support: The experience and reputation of the AI vendor are crucial. The quality of customer support is vital. Responsiveness to issues is important for long-term satisfaction.
- Ethical Considerations: A vendor’s commitment to fair AI practices is important. Active efforts to avoid bias in algorithms also matter. Adherence to responsible development principles are increasingly influential in purchasing decisions.
- Ecosystem and Partnerships: Collaborating with other tools and services in the broader digital ecosystem strengthens integrations. This can enhance the browser’s utility and appeal.
Privacy, ethics and regulatory compliance to navigate
Research indicates that “expertise,” “privacy,” “support,” and “time to value” are top criteria for selecting AI solutions. The emphasis on “trust through structure” and “source validation” for AI systems is crucial for AI browsers. Users need to trust the information. They also need to trust the actions mediated by AI. Concerns about AI knowing “too much” about users are prevalent. The need for “robust security measures” highlights this concern. These factors confirm that privacy is a major determinant. AI browser companies must deliver powerful and efficient features. They also need to cultivate a strong narrative around trust.
Additionally, ethical AI development is essential. Seamless integration into existing workflows is necessary to win over and keep users. This is vital in the competitive market.
Interviews by AI browser founders to check out:
Insights from founders highlight critical aspects of building AI tools:
Josh Miller (The Browser Company – Arc):
Emphasizes building for new user behaviors and leveraging AI to summarize public web content automatically. He acknowledges the emotional impact of rapid change. Companies need to propose solutions for economic incentives in the AI era. He also expresses concerns about potential AI regulation hindering startups.
Here is an interesting interview I came across that discussed why they moved from Arc to build AI Browser Dia, shedding light on the changing browsing space and their vision for the future:
Aravind Srinivas (Perplexity AI):
Discusses the trade-off between leveraging AI for efficiency and the potential impact on critical thinking skills, particularly in younger generations. He also touches on the ethical concerns of single entities controlling AI narratives. His focus is on building a product that is “really ready” before release, even if it means delays.
Brendan Eich (Brave):
Highlights the importance of privacy protection against tracking and fingerprinting as an ongoing commitment. He emphasizes building a browser that is easy to switch to but offers superior privacy. His vision for Brave involves a three-sided system connecting users, advertisers, and creators through the Basic Attention Token (BAT). He notes the browser’s unique position as the only universal, stable, and open cross-platform GUI that largely solves security problems.n
Subscribe for more free AI trend reports across business models and implementation
As I myself use Dia to publish my first report — I chose AI browser as our first AI trend report because I was blown away with its potential.
There are many more such AI trend analysis and data-driven stories to be covered, subscribe to get notified:
In mean time, learn more about AI Agents and LLM models from our published guides:
- MIT ChatGPT Brain Study: Explained + Use AI Without Losing Critical Thinking
- AI.gov: US AI for Governance Risks + EU AI Act Comparison
- Why Scaling Enterprise AI Is Hard – Infosys Co-Founder Nandan Nilekani Explains
- What Is Prompt Chaining? – Examples And Tutorials
- Vertical AI Agents Will Replace SaaS – Experts Warn On Future Of Workflow Automation
- Cost-efficienct AI: How Stanford built low-cost open source rival to OpenAI’s o1
- The Cost-Effective AI: Deep Dive on DeepSeek’s Game-Changing AI Engineering Approach
- Transforming Software Design with AI Agents: 2 Key Future Insights You Must Know
- 20+ insightful quotes on AI Agents and AGI from AI experts and leaders
This AI trend report is written using resources of Merrative. We are a publishing talent marketplace that helps you create publications and content libraries.
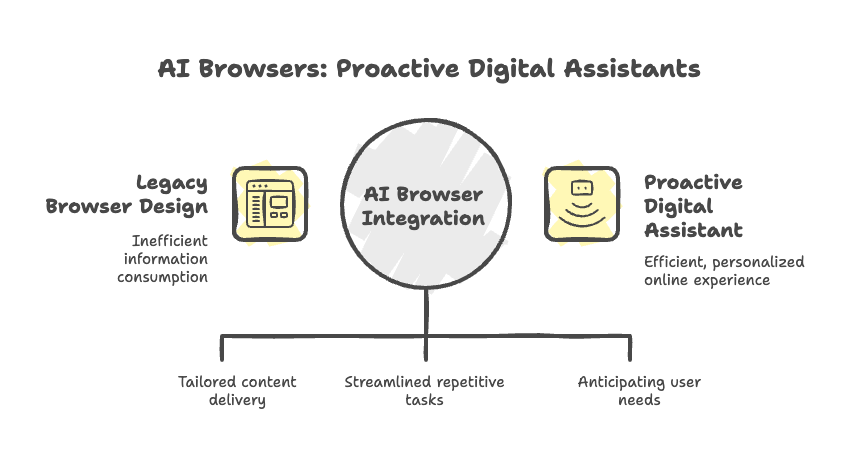
Leave a Reply